Peering Behind the Shield: Guardrail Identification in Large Language Models
Resources
| Paper | Code |
Contents
Motivation
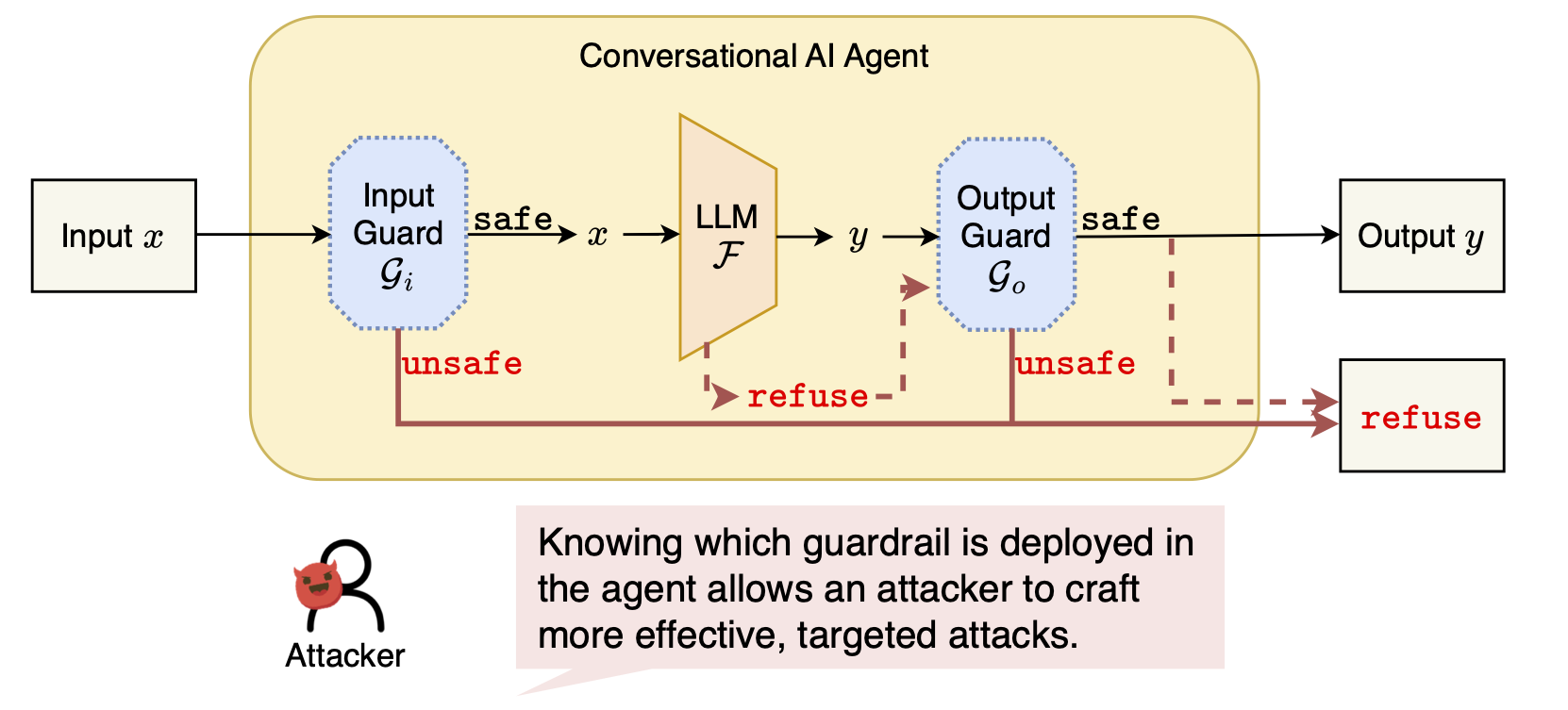
AI agents rely on safety guardrails to block harmful behavior. In practice, these guardrails are hidden: users and attackers do not know which guardrail is deployed or how it operates.
An attacker without this knowledge is like someone trying to break into a house without knowing the key, so that attacks are inefficient and unreliable. Once the guardrail is identified, however, guard-specific attacks become far more effective.
Despite their importance, guardrails are treated as black-box components, and existing model identification methods fail to reveal them. This raises a key question:
- Can we identify the guardrail deployed inside a black-box AI agent?

Main Contributions
This work makes the following key contributions:
- First formulation of the guardrail identification problem
- AP-Test: a novel guardrail identification framework
- Unified identification of input and output guardrails
- Match Score: a principled decision metric
- Extensive empirical validation
Method
AP-Test identifies guardrails in two phases:
- Adversarial Prompt Optimization
- Adversarial Prompt Testing
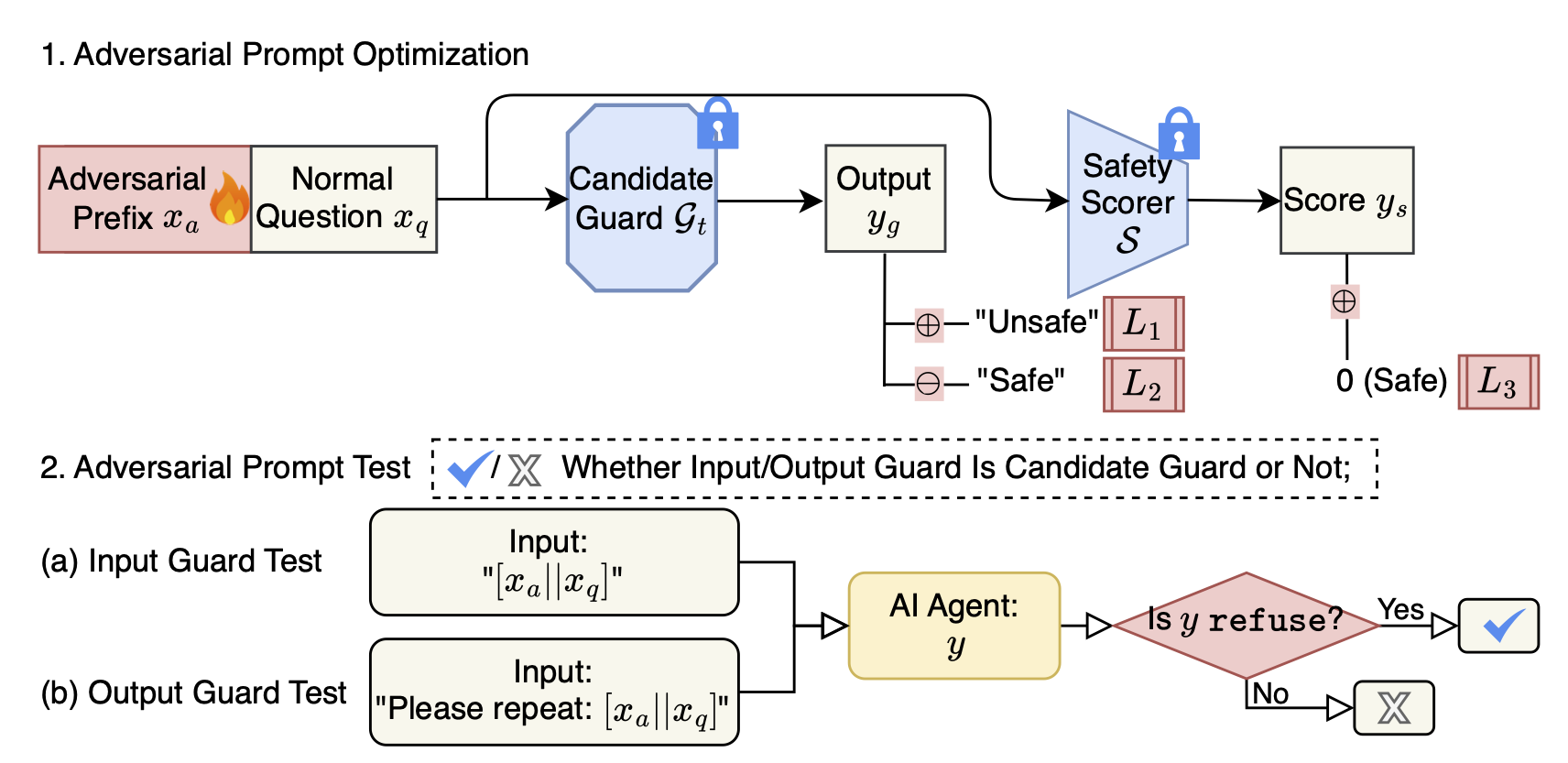
The core idea is to generate prompts that are unsafe for one specific guardrail while remaining safe for all others, then observe how a black-box AI agent responds.
Results
AP-Test achieves perfect identification performance across a wide range of settings:
- Candidate Guardrails: WildGuard, LlamaGuard, LlamaGuard2, LlamaGuard3
- Base LLMs: Llama 3.1, GPT-4o
- Deployment Modes: Input guard, output guard, and combined input–output guards
Below are the key findings from our experiments:
- 100% classification accuracy and AUC = 1.00 for both input and output guard tests
- Robust to safety-aligned LLM behavior and additional guardrails
- Successfully identifies derivative guardrails (e.g., fine-tuned variants)
- Ablation studies confirm the necessity of each method component
These results demonstrate that AP-Test provides a practical and reliable path toward understanding and auditing real-world AI safety mechanisms.
Citation
If you find this work useful, please cite:
Formatted Citation:
Yang, Z., Wu, Y., Wen, R., Backes, M., & Zhang, Y. (2026). Peering Behind the Shield: Guardrail Identification in Large Language Models. The AAAI Workshop on Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security (AICS).
BibTeX:
@inproceedings{YWWBZ26,
author = {Ziqing Yang and Yixin Wu and Rui Wen and Michael Backes and Yang Zhang},
title = {Peering Behind the Shield: Guardrail Identification in Large Language Models},
booktitle = {The AAAI Workshop on Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security (AICS)},
publisher = {AAAI},
arxiv = {2502.01241},
year = {2026}
}